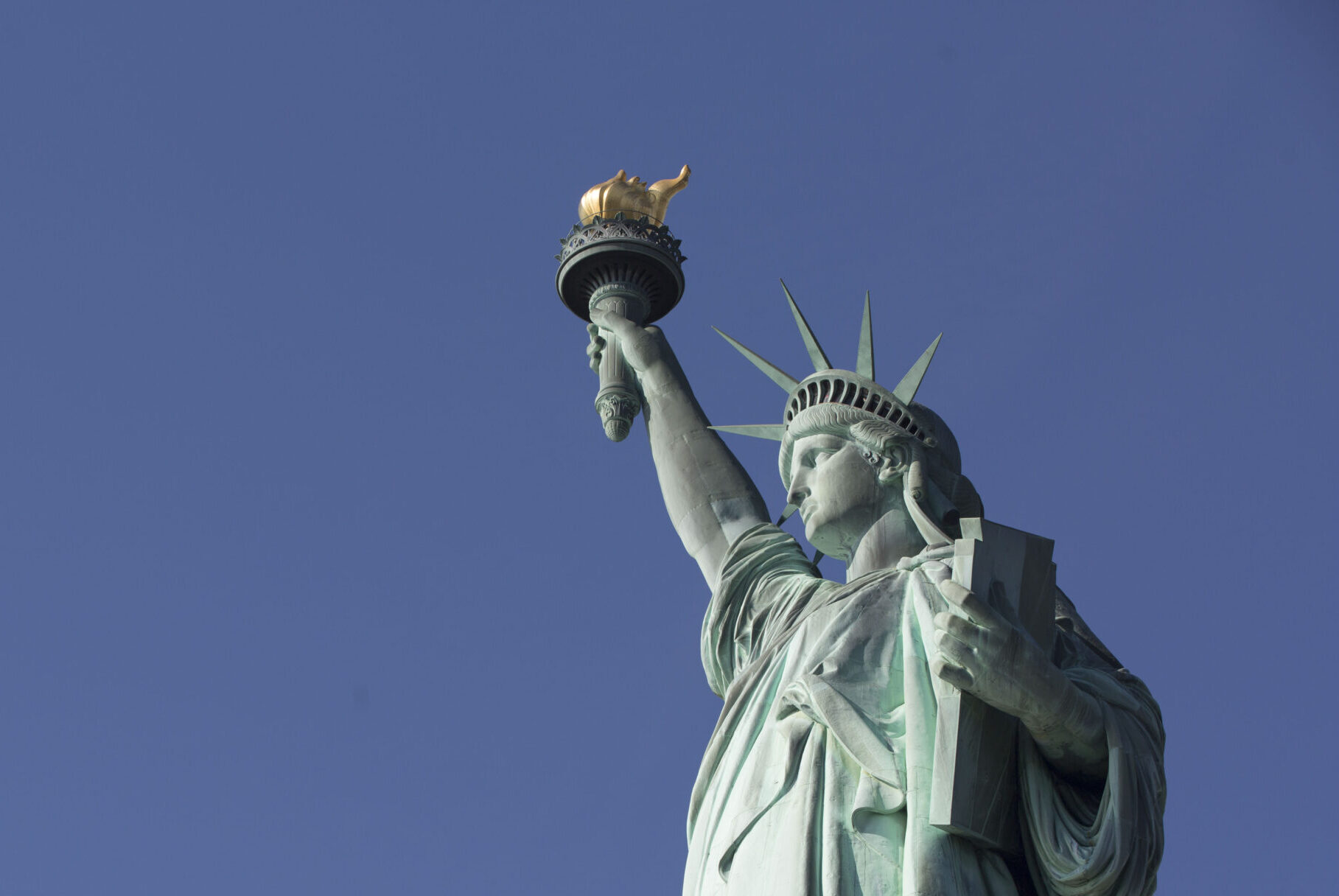



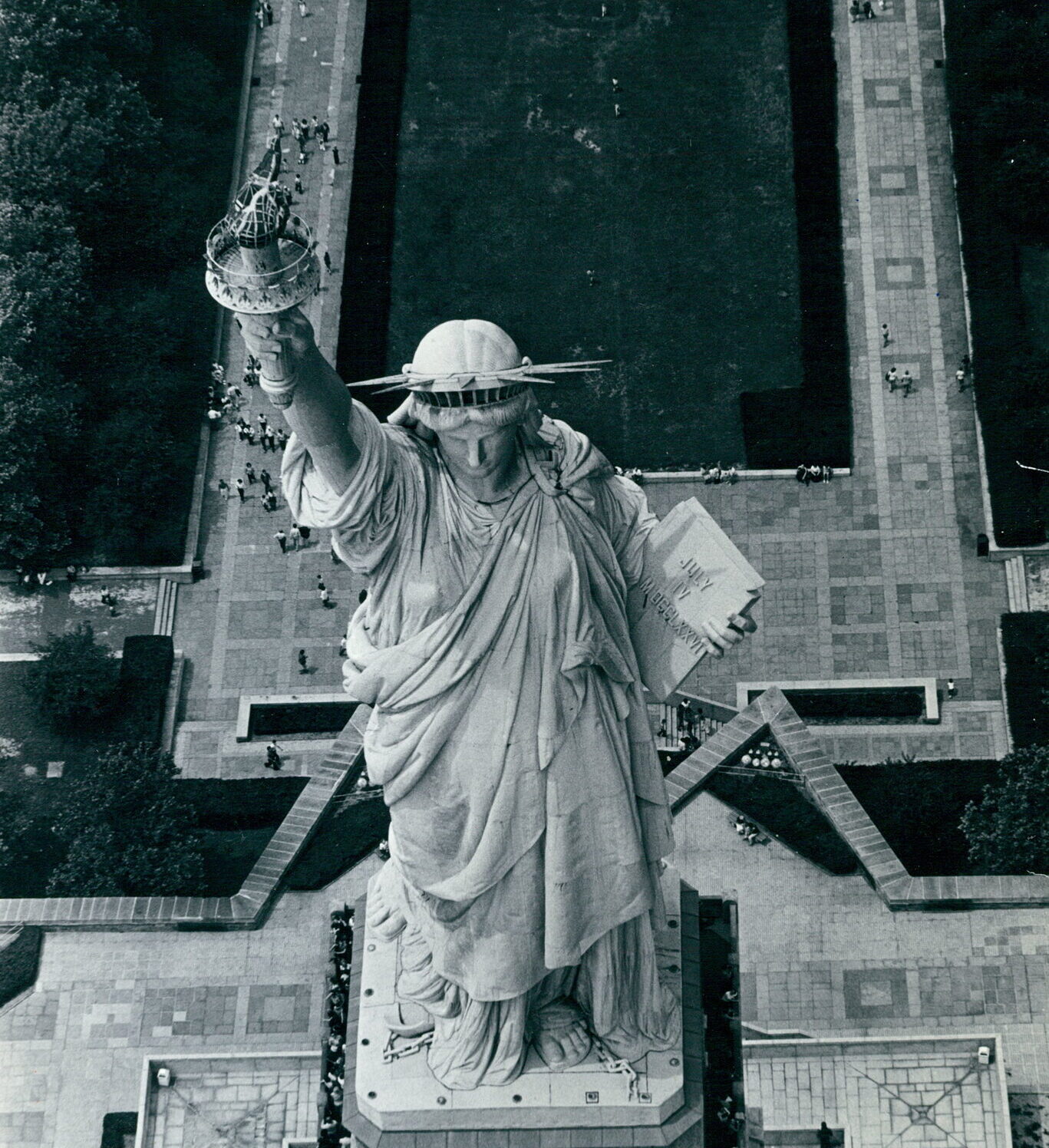





She is an icon, a national treasure, and one of the most recognizable figures in the world. Each year millions who cherish her ideals make the journey to experience her history and grandeur in person. She is the Statue of Liberty, a symbol of freedom, inspiration, and hope.
It was 1865 when Frenchman Édouard de Laboulaye proposed the idea of presenting a monumental gift from the people of France to the people of the United States. An ardent supporter of America, Laboulaye wished to commemorate the centennial of the Declaration of Independence as well as celebrate the close relationship between France and America. He was equally moved by the recent abolition of slavery in the U.S., which furthered America’s ideals of liberty and freedom.
Sculptor Frédéric-Auguste Bartholdi was in attendance for Laboulaye’s proclamation. Of like mind with Laboulaye’s cause, Bartholdi began conceptualizing the colossal structure that would soon be known as Liberty Enlightening the World.
Bartholdi’s design encompassed much symbolism: her crown representing light with its spikes evoking sun rays extending out to the world; the tablet, inscribed with July 4, 1776 in Roman numerals, noting American independence; to symbolize the end of slavery, Bartholdi placed a broken shackle and chains at the Statue’s foot.
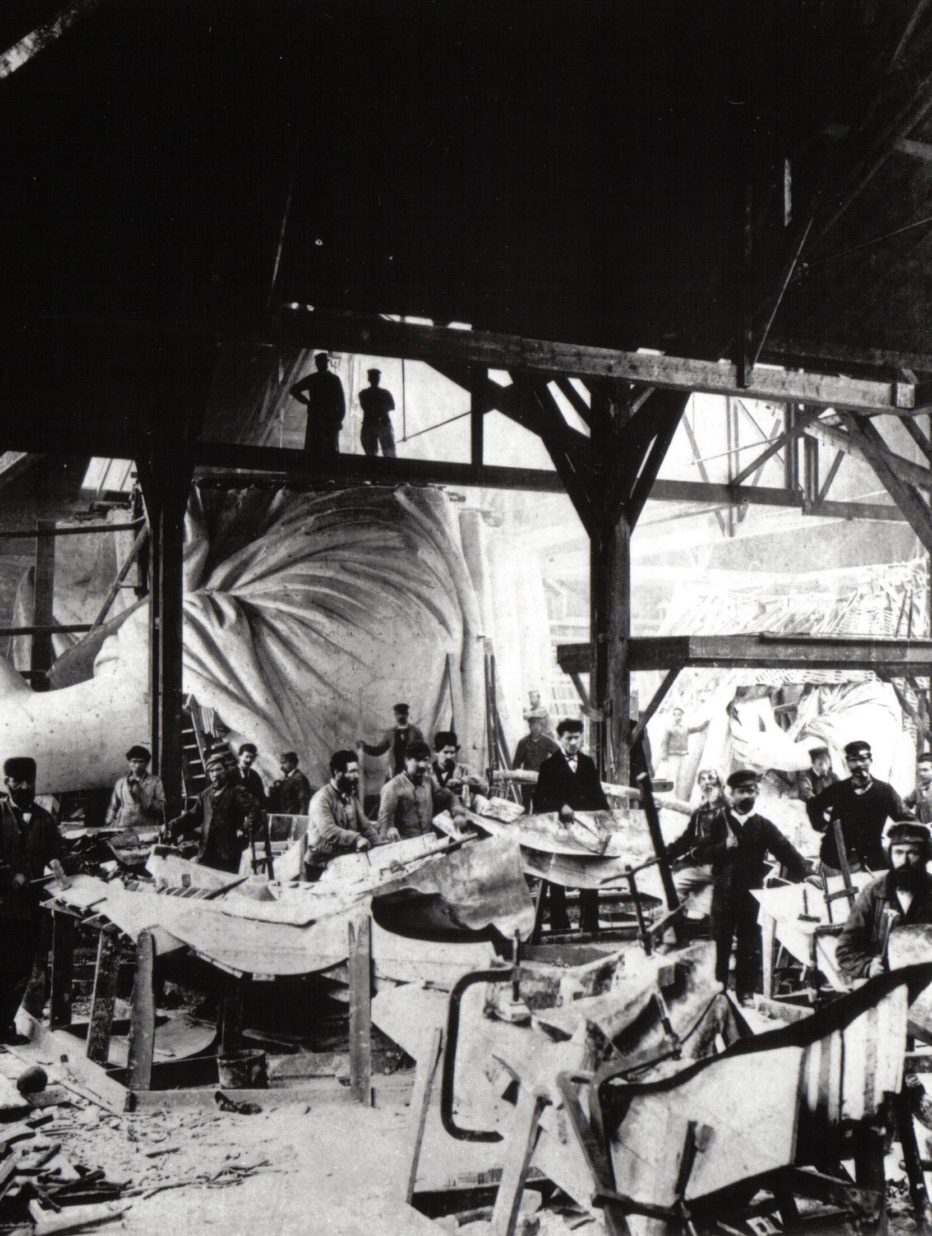
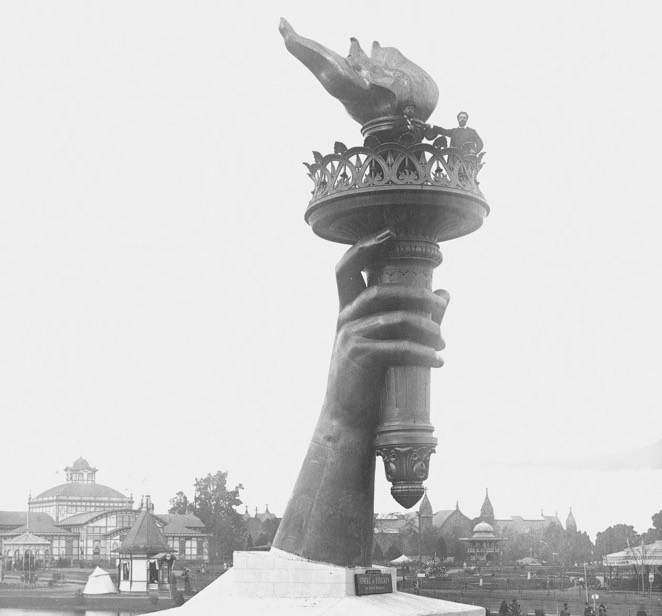


Fundraising and bringing people together have always been integral to Lady Liberty’s history. It began with efforts to finance this unprecedented undertaking. France would be responsible for creating the Statue and assembling it in the United States while the American people would fund and build the pedestal.
To raise funds in France, public fees, various forms of entertainment, and a lottery were used. In the U.S., to finance the pedestal, benefit theatrical events, art exhibitions, auctions, and prizefights were held. Poet Emma Lazarus wrote her famous sonnet The New Colossus in 1883 for an art and literary auction.
Despite these efforts, fundraising for the pedestal went slowly. To spark public action, in 1885, Joseph Pulitzer placed an ad in his paper the New York World inviting readers to donate to the cause. In exchange, Pulitzer printed each donor’s name in the newspaper. The public rose to the challenge with 120,000 people donating over $100,000 and securing the remaining funds needed for the Statue’s pedestal.
Meanwhile in France, Bartholdi required the assistance of an engineer to address structural issues associated with designing such a colossal copper sculpture. Alexandre Gustave Eiffel, just prior to creating his famed Tower, was engaged to design the massive iron pylon and secondary skeletal framework that allows the Statue’s copper skin to move independently yet stand upright.
Construction of the Statue was completed in France in July 1884. The massive sculpture stood tall above the rooftops of Paris awaiting her voyage across the sea.
Back in America that same year architect Richard Morris Hunt was selected to design the Statue’s granite pedestal, and construction got underway.
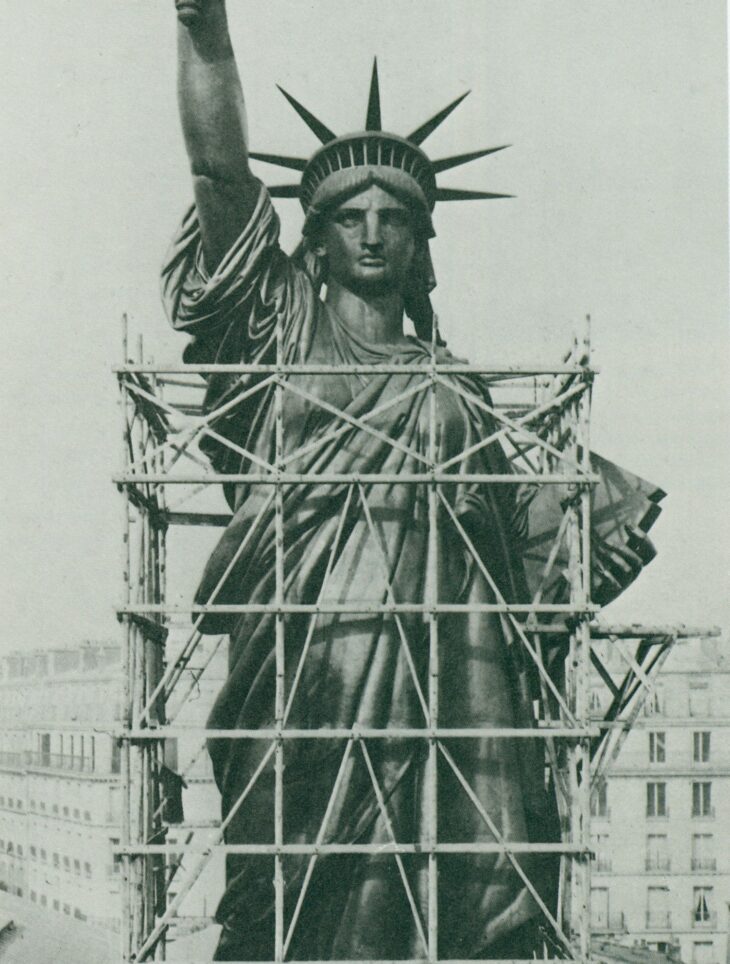


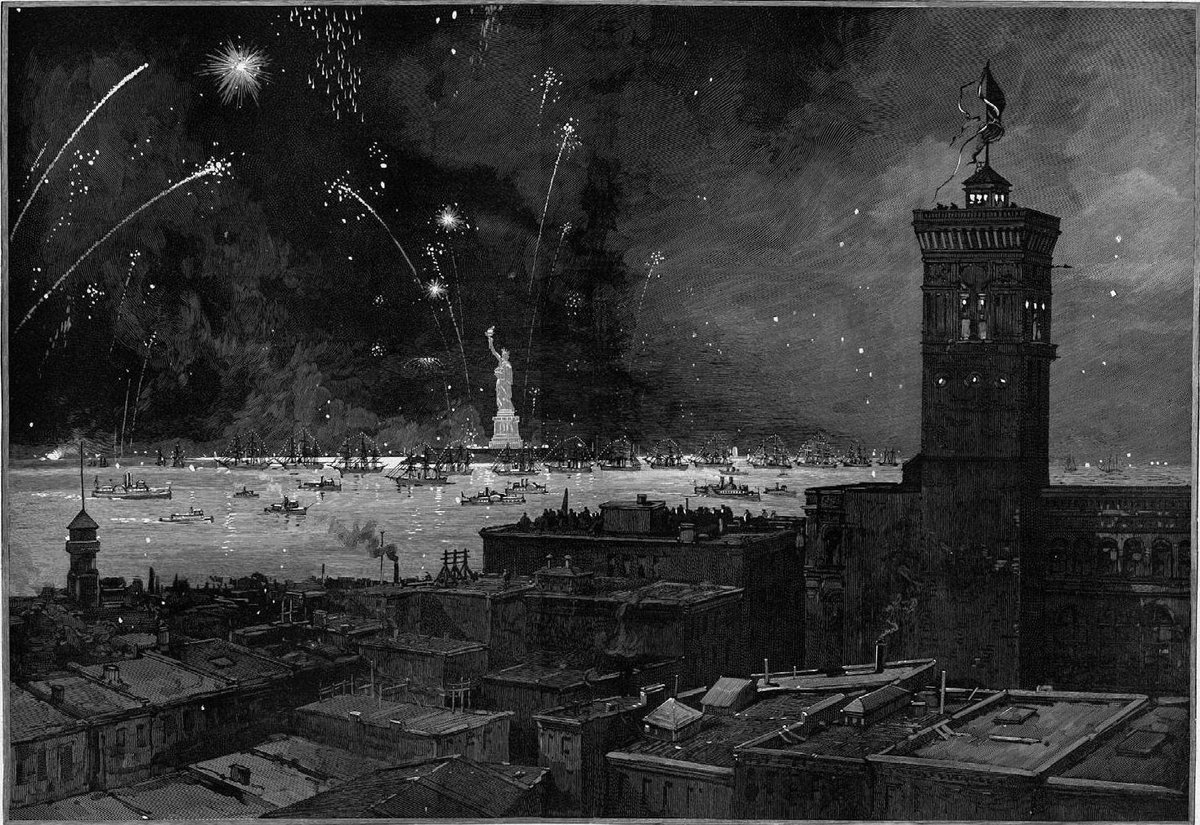
For its trans-Atlantic voyage aboard the frigate Isère, the Statue was reduced to 350 individual pieces and packed in 214 crates. The ship arrived in New York Harbor on June 17, 1885. While awaiting construction of its pedestal, the Statue remained in pieces on what was then called Bedloe’s Island. The pedestal was completed in April 1886 and finally, on October 28, 1886, President Grover Cleveland oversaw the dedication of the Statue of Liberty in front of thousands of spectators.
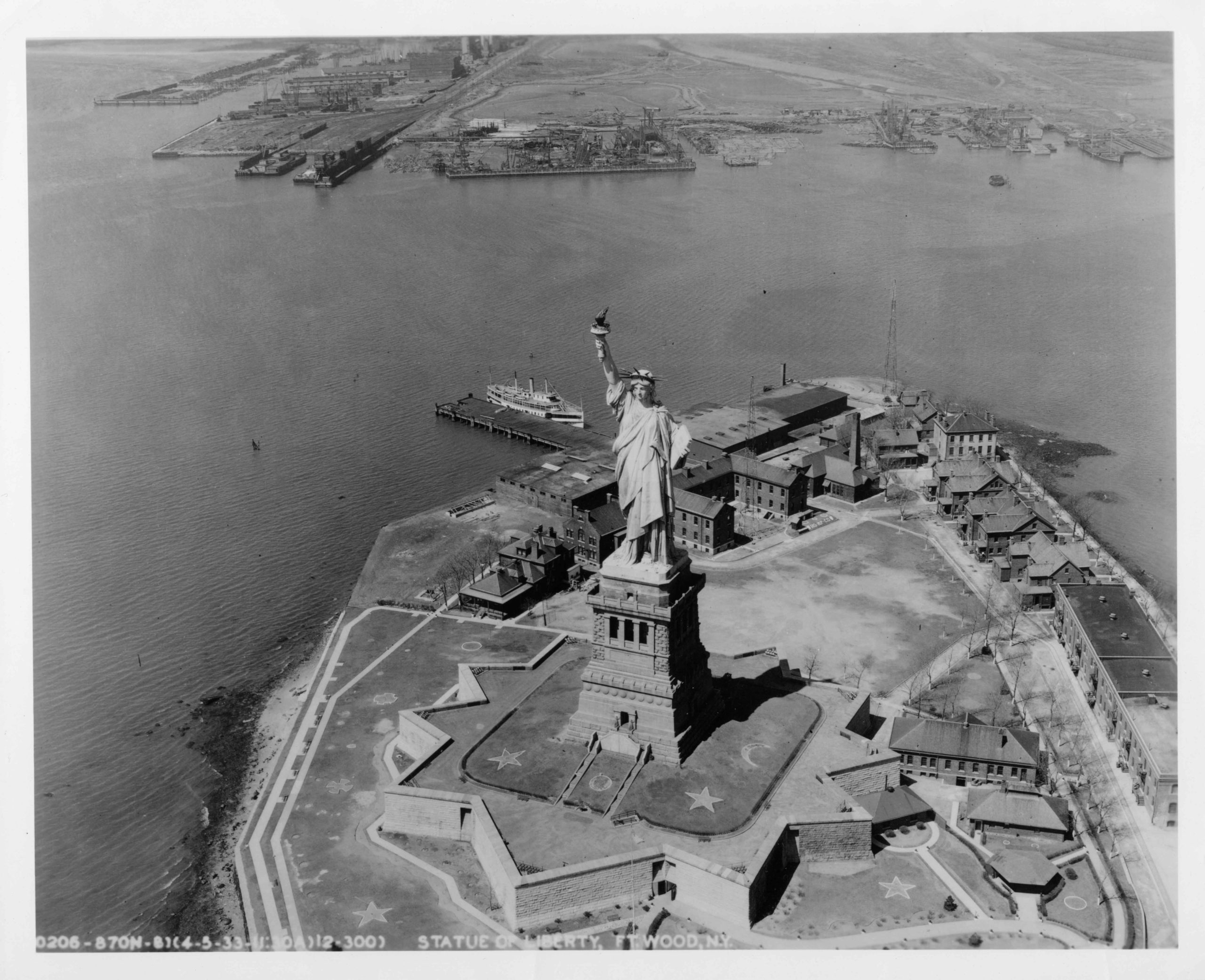
The story of the Statue of Liberty and her island has been one of change. For centuries the island was a major source of food for the Lenape native people and later Dutch settlers. In 1807, the U.S. Army deemed the island a military post, constructing an 11-point fort to protect New York Harbor. Later renamed Fort Wood, the structure now serves as the base for the Statue’s pedestal. The Statue’s own meaning and relevance have evolved with time, as well. Perhaps most notable is the association with welcoming “huddled masses.” In 1903, a plaque engraved with “The New Colossus” was placed in the pedestal. With that Lady Liberty’s significance grew as an inspiration to immigrants who sailed past her on their way to America.
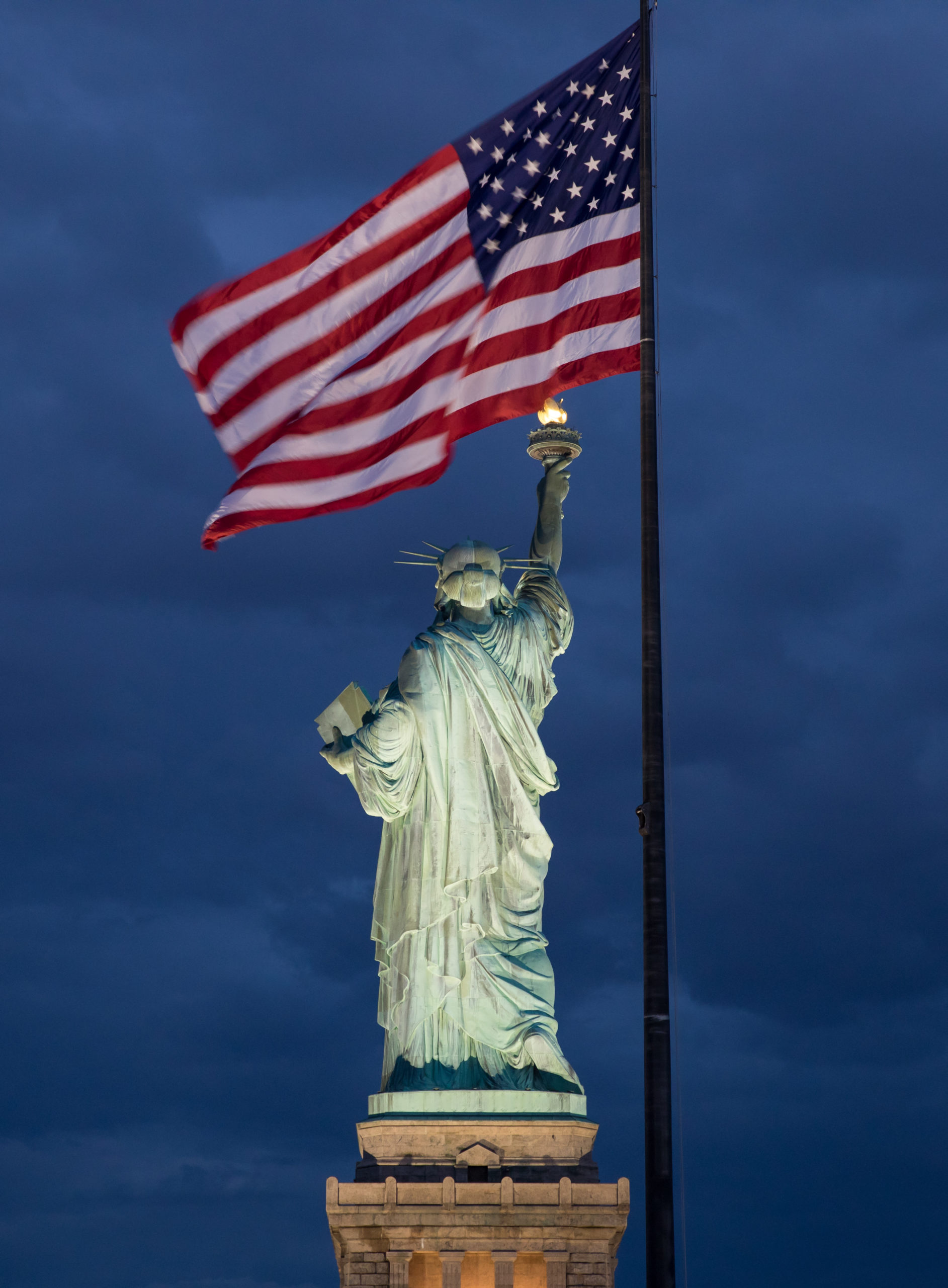
As Bartholdi envisioned it in 1874, the flame of the Statue’s torch was not to be lighted but rather made of solid copper sheet and gilded to shine brightly in daylight. But during its first half-century, the torch underwent numerous modifications. When the Statue was dedicated in 1886, two rows of portholes had been cut from the copper at the bottom of the torch to illuminate it from inside. Six years later, an 18-inch belt of glass replaced the upper row of portholes and an octagonal pyramidal skylight with red, white and yellow glass was installed on top of the flame. Changes continued in 1916 when copper was removed in about 250 places and replaced with amber-colored cathedral glass. In 1931 a new lighting system was installed that called for two holes 16 inches in diameter to be cut into the floor of the balcony around the flame through which two projectors were installed. By this time, Bartholdi’s design was barely recognizable.
In the 1980s when the Foundation was restoring the Statue for its centennial celebration, a team of experts determined that the original torch could not be restored. A century of modifications had radically altered Bartholdi’s solid copper flame to one mainly of glass. Leaks from rain and corrosion from the elements had damaged the original torch above the handle beyond repair and it was removed on July 4, 1984.
In November 1985, a replica of Bartholdi’s original design was installed onto the Statue and formally dedicated during the July 4, 1986, Liberty Weekend centennial celebration.
Today, the original torch is on display in the Inspiration Gallery of the Statue of Liberty Museum.